Comprehensive Analysis of EGFRMutant Abundance and Its Effect on Efficacy of EGFR TKIs in Advanced NSCLC with EGFR Mutations
Background
It is not enough sensitive to use a qualitative detection method with sensitivity of 1% to determine EGFR status in advanced NSCLC and guide precise therapy in clinical practice. Objective: To explore the relationship between the abundance of EGFR mutations and efficacy of EGFR-TKIs.
Methods
We used ARMS plus (ARMS+) to quantitatively evaluate the abundance of EGFR mutations in 201 advanced NSCLC patients. A cut-off value of the abundance of EGFR mutations was determined by ROC analysis in training group and was validated in validation group.
Result
The abundance of EGFR activating mutation by ARMS+ was significantly associated with objective response to EGFR-TKIs. The abundance of 19DEL was significantly higher than that of L858R, with the cutoff values for 19DEL and L858R were 4.9% and 9.5%, respectively. The median PFS in Hi group was significantly longer than those in Lo group (19DEL, 15.0 vs 2.0 months, P < 0.001; L858R, 12.3 vs. 2.0 months, P < 0.001) in the training set. Similar results were also observed in validation set. 9 of 13 patients harboring T790M mutation achieved PR to EGFR-TKIs. The majority (7/9) were identified to be with low abundance of T790M mutation. The abundance of EGFR mutations appeared to be more significantly associated with the copy number of EGFR mutations from ctDNA in 19DEL group.
Conclusion
The abundance of EGFR activating mutation by ARMS+ was significantly associated with objective response to EGFR-TKIs. The abundance of EGFRT790M mutation may have an adverse impact on PFS rather than ORR in advanced EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients treated with EGFR-TKIs.
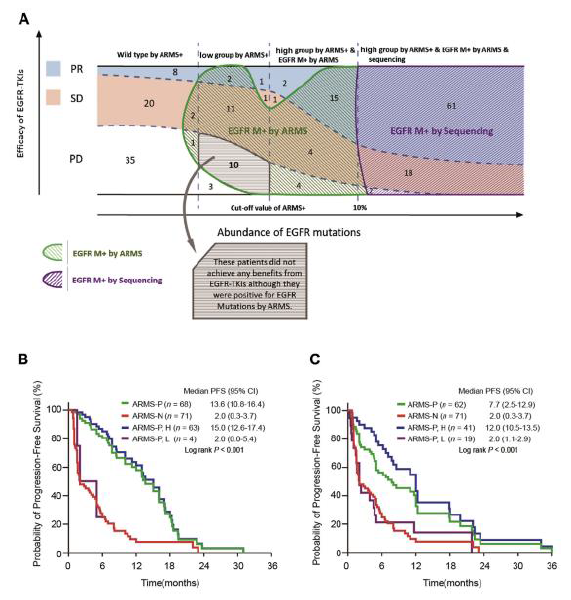
Figure: The difference in response to EGFR (tyrosine kinase inhibitors) TKIs and progression-free survival in response to EGFR TKIs between patients with EGFR wild-type NSCLC and those with EGFR-mutant NSCLC identified by the amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS) optimized with competitive blockers and specific mutation quantitation (ARMSþ), ARMS, and sequencing. The patients with EGFR mutations by ARMS but low abundance of EGFR mutations by ARMSþ from tumor tissues may achieve few benefits from EGFR TKIs. (A) The percentages of patients who achieved a partial response, stable disease, or progressive disease differed with the change of abundance of EGFR mutations in this study (numerals are numbers of patients). Progression-free survival of the groups stratified according to specific mutation status for exon 19 deletions (B) and L858R (C) by the ARMS method and ARMSþ. ARMS-P, positive group with a positive result by ARMS; ARMS-N, group with a negative result by ARMS; ARMS-P, H, patients with a mutation abundance higher than or equal to the cutoff by ARMSþ in the ARMS-P group; ARMS-P, L, patients with mutation abundance lower than the cutoff and greater than 0.1% by ARMSþ in the ARMS-P group; CI, confidence interval.


